二叉树-31-37对称二叉树
31. 对称的二叉树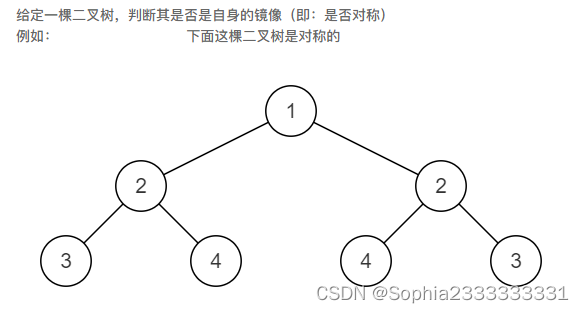

递归:
把原问题化成更小规模的问题,并且具有相同的问题性质,重复调用本身函数
二叉树的递归,是将某个节点的左子树、右子树看成一颗完整的树,那么对于子树的访问或者操作就是对于原树的访问或者操作的子问题,因此可以自我调用函数不断进入子树。
- 终止条件: 当进入子问题的两个节点都为空,说明都到了叶子节点,且是同步的,因此结束本次子问题,返回true;当进入子问题的两个节点只有一个为空,或是元素值不相等,说明这里的对称不匹配,同样结束本次子问题,返回false。
- 返回值: 每一级将子问题是否匹配的结果往上传递。
- 本级任务: 每个子问题,需要按照上述思路,“根左右”走左边的时候“根右左”走右边,“根左右”走右边的时候“根右左”走左边,一起进入子问题,需要两边都是匹配才能对称。
import java.util.*;
/*
public class TreeNode {int val = 0;TreeNode left = null;TreeNode right = null;public TreeNode(int val) {this.val = val;}
}
*/
public class Solution {boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode pRoot) {return resu(pRoot,pRoot); }boolean resu(TreeNode p1, TreeNode p2){if(p1==null&&p2==null){return true;}if(p1==null||p2==null||p1.val!=p2.val) return false;//注意p1.val!=p2.val一定要放在或的最后一个return resu(p1.left, p2.right)&&resu(p1.right, p2.left);}
}
注意p1.val!=p2.val一定要放在或的最后一个,否则当有一个为null时就会出现异常。
时间复杂度和空间复杂度都是O(N)
32.合并二叉树
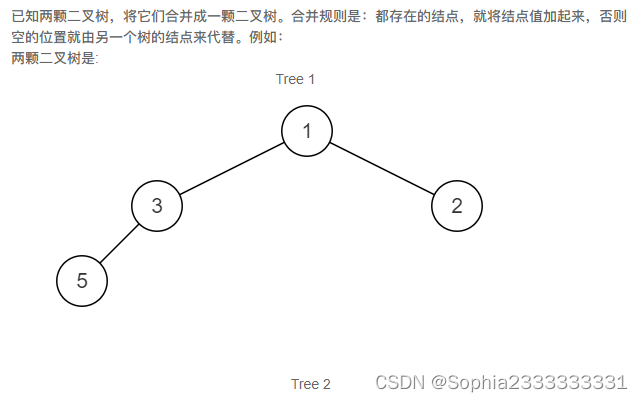
递归
import java.util.*;/** public class TreeNode {* int val = 0;* TreeNode left = null;* TreeNode right = null;* }*/public class Solution {/*** * @param t1 TreeNode类 * @param t2 TreeNode类 * @return TreeNode类*/public TreeNode mergeTrees (TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {// write code hereif(t1==null) return t2;if(t2==null) return t1;TreeNode head = new TreeNode(t1.val+t2.val);head.left = mergeTrees(t1.left,t2.left);head.right = mergeTrees(t1.right,t2.right);return head;}
}
时间复杂度和空间复杂度都是O(N)
33. 二叉树的镜像

递归的话,每次都交换节点的左右子树
import java.util.*;/** public class TreeNode {* int val = 0;* TreeNode left = null;* TreeNode right = null;* public TreeNode(int val) {* this.val = val;* }* }*/public class Solution {/*** 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可** * @param pRoot TreeNode类 * @return TreeNode类*/public TreeNode Mirror (TreeNode pRoot) {// write code hereif(pRoot==null) return null;TreeNode node = pRoot.left;pRoot.left = pRoot.right;pRoot.right = node;Mirror(pRoot.left);Mirror(pRoot.right);return pRoot;}
}
时间复杂度和空间复杂度都是O(N),没找到空间复杂度为O(1)的解法。
递归本质上是深搜,广搜可以用队列或者栈来解决。思路是每次出堆、栈的元素的时候,交换该节点的左右节点
用队列
import java.util.*;/** public class TreeNode {* int val = 0;* TreeNode left = null;* TreeNode right = null;* public TreeNode(int val) {* this.val = val;* }* }*/public class Solution {/*** 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可** * @param pRoot TreeNode类 * @return TreeNode类*/public TreeNode Mirror (TreeNode pRoot) {// write code hereQueue q = new ArrayDeque<>();if(pRoot==null) return null;q.offer(pRoot);while(!q.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = q.poll();TreeNode tmp = node.left;node.left = node.right;node.right = tmp;if(node.left!=null) q.offer(node.left);if(node.right!=null) q.offer(node.right);}return pRoot;}
}
用栈:
import java.util.*;/** public class TreeNode {* int val = 0;* TreeNode left = null;* TreeNode right = null;* public TreeNode(int val) {* this.val = val;* }* }*/public class Solution {/*** 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可** * @param pRoot TreeNode类 * @return TreeNode类*/public TreeNode Mirror (TreeNode pRoot) {// write code hereStack q = new Stack<>();if(pRoot==null) return null;q.push(pRoot);while(!q.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = q.pop();TreeNode tmp = node.left;node.left = node.right;node.right = tmp;if(node.left!=null) q.push(node.left);if(node.right!=null) q.push(node.right);}return pRoot;}
}
只要全都翻转一遍即可,至于先后顺序不重要,所以这里用队列和栈是完全一样的,时间空间都是O(N)
34. 判断是不是二叉搜索树
第一次用递归true和false的方法,只能判断当前节点和左右子节点的关系,不能保证所有的子孙节点。
思路:用中序遍历,存成数组后判断数组是不是递增的。
import java.util.*;/** public class TreeNode {* int val = 0;* TreeNode left = null;* TreeNode right = null;* public TreeNode(int val) {* this.val = val;* }* }*/public class Solution {/*** 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可** * @param root TreeNode类 * @return bool布尔型*/public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) {// write code hereArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();inorder(list,root);for(int i = 0; i < list.size()-1; i++){if(list.get(i) >= list.get(i+1)) return false;}return true;}public void inorder(ArrayList list, TreeNode root){if(root==null) return ;inorder(list,root.left);list.add(root.val);inorder(list,root.right);return;}
}
另一种递归做法
step 1:首先递归到最左,初始化maxLeft与pre。
step 2:然后往后遍历整棵树,依次连接pre与当前节点,并更新pre。
step 3:左子树如果不是二叉搜索树返回false。
step 4:判断当前节点是不是小于前置节点,更新前置节点。
step 5:最后由右子树的后面节点决定。
这样不需要额外的数组存,不需要每次都遍历完,只要每次遍历到的时候判断和前一个节点值的大小即可
import java.util.*;/** public class TreeNode {* int val = 0;* TreeNode left = null;* TreeNode right = null;* public TreeNode(int val) {* this.val = val;* }* }*/public class Solution {/*** 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可** * @param root TreeNode类 * @return bool布尔型*/int pre = Integer.MIN_VALUE;public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) {// write code hereif(root==null) return true;//先判断左子树if(!isValidBST(root.left)) return false;if(root.val<=pre) return false;pre = root.val;//右子树return isValidBST(root.right);}}
35. 判断是不是完全二叉树
用队列实现的层次遍历,用LinkedList可以存储null,标记第一次出现null,之后再遇到就返回false
import java.util.*;/** public class TreeNode {* int val = 0;* TreeNode left = null;* TreeNode right = null;* public TreeNode(int val) {* this.val = val;* }* }*/public class Solution {/*** 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可** * @param root TreeNode类 * @return bool布尔型*/public boolean isCompleteTree (TreeNode root) {// write code hereQueue q = new LinkedList<>();q.offer(root); boolean flag = false;while(!q.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = q.poll();if(node==null){flag = true;continue;}if(flag) return false;q.offer(node.left);q.offer(node.right); }return true; }
}
ArrayDeque类是可变数组的实现,不可存储null。LinkedList是线性表的实现,实现了线性表的所有操作,可存储null
这里不能用ArrayDeque!!!
36. 判断是不是平衡二叉树
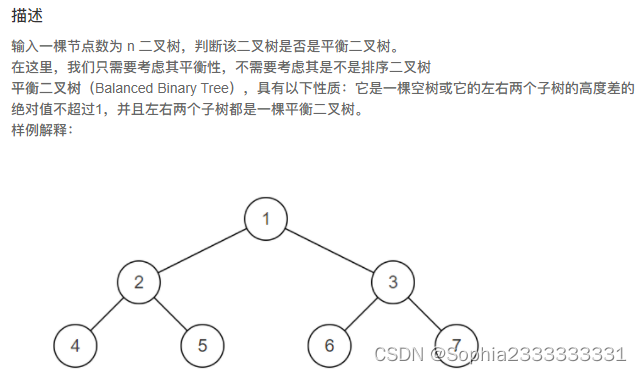
在求树的深度的基础上进行改进
二叉树求树的深度的代码:
public int TreeDepth(TreeNode root) {if(root == null)return 0;int l = TreeDepth(root.left);int r = TreeDepth(root.right);return Math.max(l,r)+1;}
在这个基础上加上判断左右子树高度差超过1:
boolean isBalanced = true; // 默认标记为truepublic boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root) {TreeDepth(root);return isBalanced;}public int TreeDepth(TreeNode root) {if(root == null)return 0; // 递归终止int l = TreeDepth(root.left);int r = TreeDepth(root.right);if(Math.abs(l-r) > 1){isBalanced = false; // 不是平衡树}return Math.max(l,r)+1; // 求深度}
但是这样总是会遍历完所有的节点,我们可以进行改进,边求深度边判断
public class Solution {public boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root) {return depth(root)!=-1;}public int depth(TreeNode root){if (root==null) return 0;int l = depth(root.left);if(l==-1) return -1;int r = depth(root.right);if(r==-1) return -1;if(Math.abs(l-r)>1) return -1;return Math.max(l,r)+1; }
}
时间和空间复杂度都是O(N)
37. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先

import java.util.*;/** public class TreeNode {* int val = 0;* TreeNode left = null;* TreeNode right = null;* public TreeNode(int val) {* this.val = val;* }* }*/public class Solution {/*** 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可** * @param root TreeNode类 * @param p int整型 * @param q int整型 * @return int整型*/public int lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int p, int q) {// write code here//第一次进入不同的分支就找到了if((proot.val&&q>root.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);return root.val;}
}