JUC系列(九) CAS 与锁的理解
📣 📣 📣 📢📢📢
☀️☀️你好啊!小伙伴,我是小冷。是一个兴趣驱动自学练习两年半的的Java工程师。
📒 一位十分喜欢将知识分享出来的Java博主⭐️⭐️⭐️,擅长使用Java技术开发web项目和工具
📒 文章内容丰富:覆盖大部分java必学技术栈,前端,计算机基础,容器等方面的文章
📒 如果你也对Java感兴趣,关注小冷吧,一起探索Java技术的生态与进步,一起讨论Java技术的使用与学习
✏️高质量技术专栏专栏链接: 微服务,数据结构,netty,单点登录,SSM ,SpringCloudAlibaba等
😝公众号😝 : 想全栈的小冷,分享一些技术上的文章,以及解决问题的经验
⏩当前专栏:JUC系列
深入理解CAS
什么是 CAS
CAS compareAndSet 比较并交换
研究底层,才会有所突破
实例代码
//CAS compareAndSet 比较并交换public static void main(String[] args) {AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(2020);// 两个参数 : 期望 更新// public final boolean compareAndSet(int expectedValue, int newValue)// 如果我们的期望值达到了 那么就更新,否则 就不更新 CAS 是 CPU 并发原语atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2020, 2021);System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());atomicInteger.getAndIncrement();atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2020, 2021);System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());}
加一 方法底层原理 为什么效率高
- 调用了 unsafe 操作内存的方法
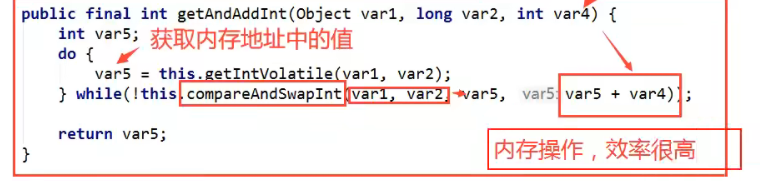
- 查看这个getAndAddInt这个方法的参数, var 1 就是原本数字 var 2 就是valueoffset ,var 4 就是要增加多少
- var 是获取内存值,之后调用方法 如果 var1 和 var2 的结果是我们想要的 也就是 var5 那么就讲 var5+var4 也就是原本的结果 +1
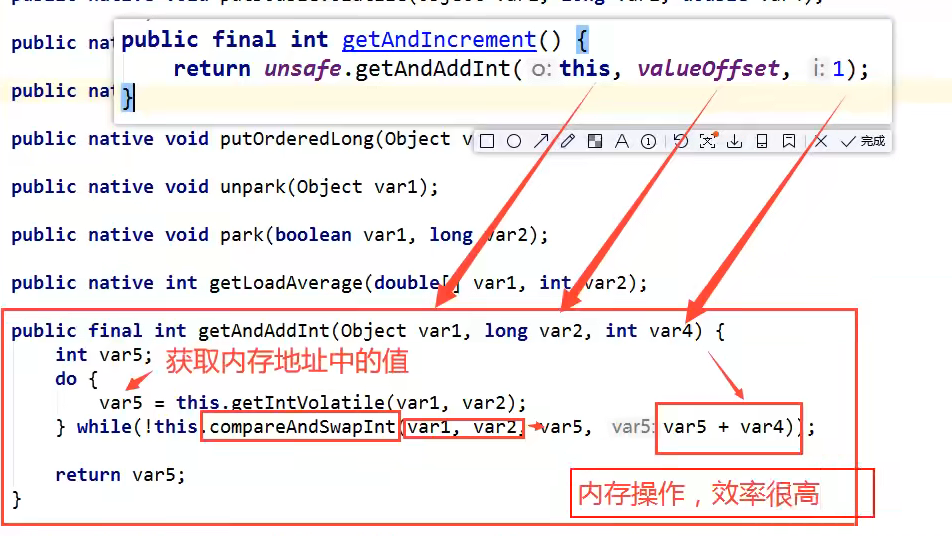
这个方法是一个典型的自旋锁
CAS:比较当前工作内存中的值,如果这个值是期望的,那么执行操作,如果不是就一直循环
缺点:
- 循环会耗时
- 一次性只能保证一个共享变量
- ABA问题
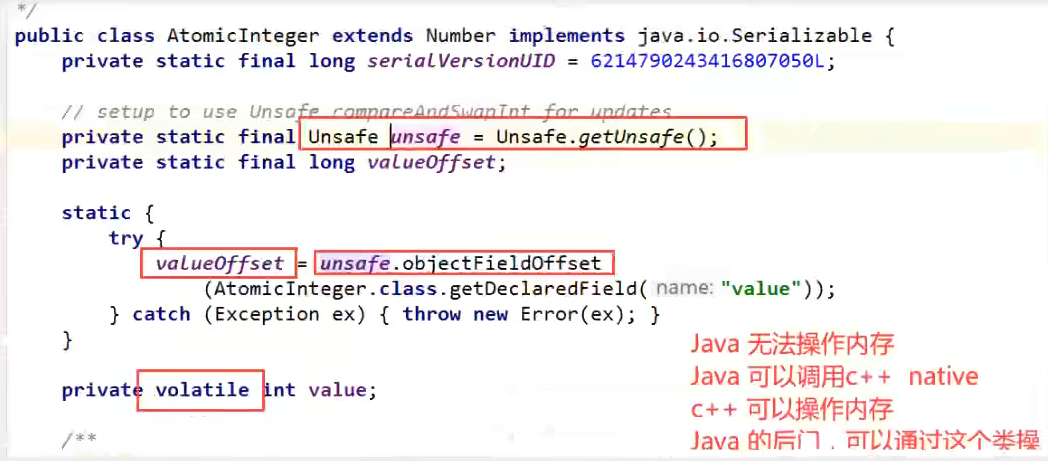
unsafe类
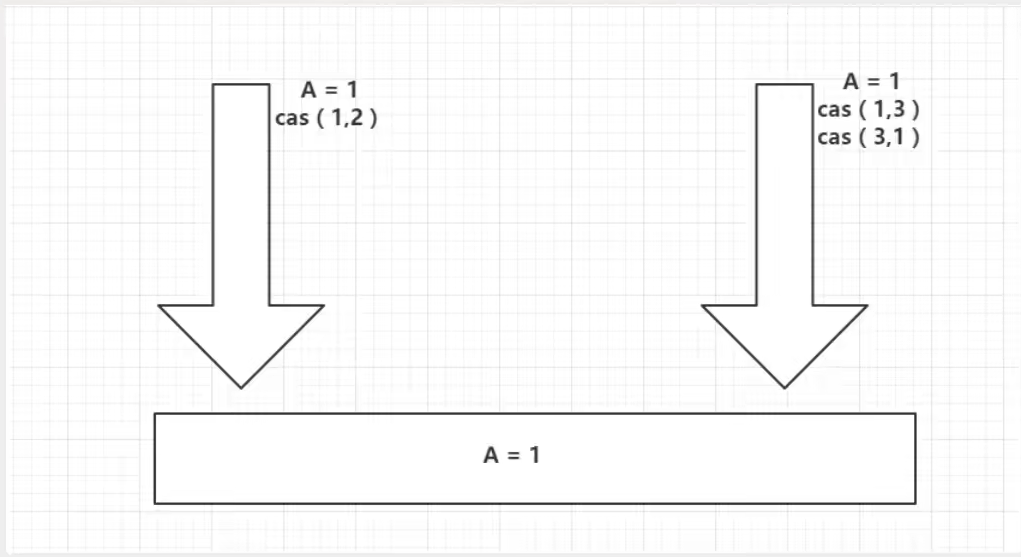
CAS ABA问题
A:期望是 1 交换成2 ,但是在还没有交换的时候 另一个线程 把 当前的a 改变成了 3 又改回 1 此时 当前A线程依旧可以正常的交换,但是期间的值已经被别人用过了。
//CAS compareAndSet 比较并交换public static void main(String[] args) {AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(2020);//对于 我们平时都 sql 是如何解决的,乐观锁// 两个参数 : 期望 更新// public final boolean compareAndSet(int expectedValue, int newValue)// 如果我们的期望值达到了 那么就更新,否则 就不更新 CAS 是 CPU 并发原语//=============捣乱的线程====================atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2020, 2021);System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2021, 2020);System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());//=================期望的线程=============atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2020, 2021);System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());}
原子引用(解决aba问题)
解决ada问题
原子引用
AtomicStampedReference
可以理解为 乐观锁
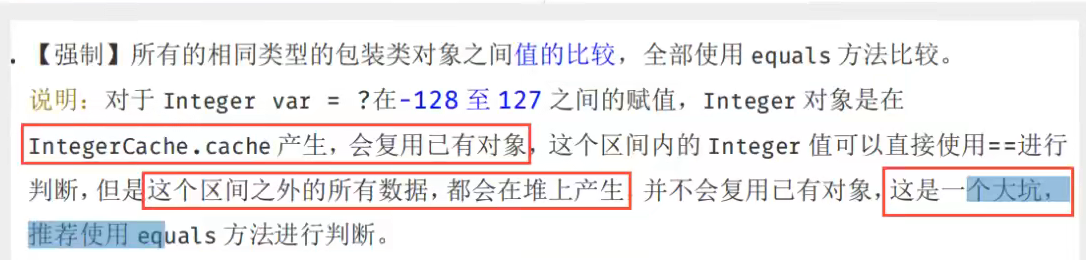
PS: integer 使用了 对象缓存机制,默认范围是 -128-127 ,推荐使用静态工厂方法 valueof 获取对象实例,而不是new ,因为 value of 使用缓存,而new 一定会创建心的对象分配新的内存空间
代码实例
//CAS compareAndSet 比较并交换public static void main(String[] args) {//AtomicInteger atomicStampedReference = new AtomicInteger(2020);// 注意 如果 泛型是一个包装类,注意对象的引用问题,AtomicStampedReference atomicStampedReference = new AtomicStampedReference<>(1, 1);new Thread(() -> {int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp();System.out.println("a1 =>" + stamp);System.out.println("a2 =>" + atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(1, 2, atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1));System.out.println("a2 =>" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());System.out.println("a3 =>" + atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(2, 1, atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1));System.out.println("a3 =>" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());}, "a").start();new Thread(() -> {int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp();System.out.println("b1 =>" + stamp);try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("b2 =>" + atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(1, 6, atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1));System.out.println("b2 =>" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());}, "b").start();}
对于锁的理解
1、公平锁和非公平锁的区别
公平锁 :不能够插队,必须先来后到
非公平锁: 可以插队 锁 默认的都是非公平的
public ReentrantLock() {sync = new NonfairSync();}也可以修改成 公平锁
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();}2、可重入锁
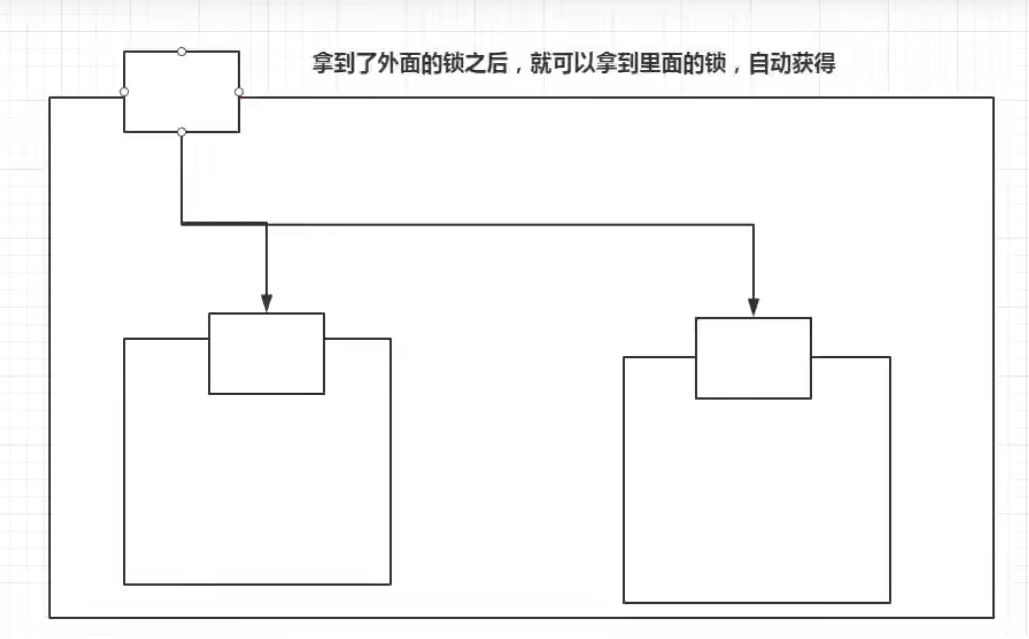
sync关键字
这里 是一把锁,每次执行的时候直到方法里逐层向外解锁
public class lockdemo {public static void main(String[] args) {phone phone = new phone();new Thread(() -> {phone.sms();}, "a").start();new Thread(() -> {phone.sms();}, "b").start();}
}class phone {public synchronized void sms() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>发短信");//这里也有锁call();}public synchronized void call() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>打电话");}
}Lock
- lock 锁每个方法是配对一个锁,像下面的例子就是开了两个锁,锁必须配对
public class lockdemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {phone2 phone = new phone2();new Thread(() -> {phone.sms();}, "a").start();new Thread(() -> {phone.sms();}, "b").start();}
}class phone2 {//这里就有区别 sync关键字是一个锁,这里使用lock 是两个锁,锁必须配对,否则就会死锁Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();public synchronized void sms() {lock.lock();try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>发短信");//这里也有锁call();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.unlock();}}public synchronized void call() {lock.lock();try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>打电话");//这里也有锁call();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.unlock();}}
}3、自旋锁
这里我们之前查看CAS 的时候 有一个调用自增的方法就是自旋锁
自己的简易自旋锁
public class spinlocks {// int =0
// thread = nullAtomicReference atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>();// 加锁操作public void mylock() {Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();System.out.println(thread.getName() + "=> mylock");while (!atomicReference.compareAndSet(null, thread)) {}}// 解锁public void myunlock() {Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();System.out.println(thread.getName() + "=> myUnlock");atomicReference.compareAndSet(thread, null);}
}class test {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//底层使用 CAS 自旋锁spinlocks lock = new spinlocks();new Thread(() -> {lock.mylock();try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.myunlock();}}, "t1").start();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);new Thread(() -> {lock.mylock();try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.myunlock();}}, "t2").start();}
} 4、死锁
什么是死锁: 互相争抢锁的过程
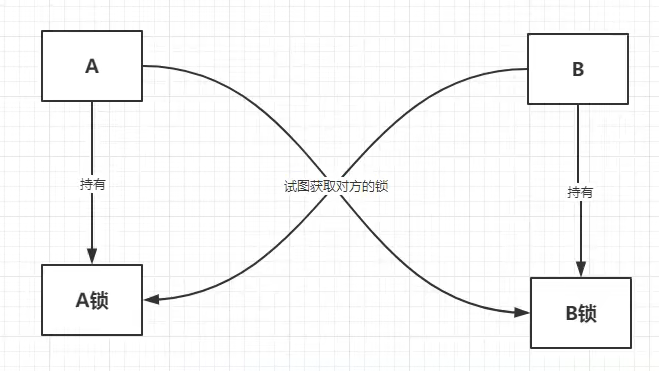
死锁测试,如何排查死锁
public class DeadLockDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {String a = "lockA";String b = "lockB";new Thread(new mythread(a, b), "t1").start();new Thread(new mythread(b, a), "t2").start();}
}class mythread implements Runnable {private String a;private String b;public mythread(String a, String b) {this.a = a;this.b = b;}@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (a) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "lock=>" + a + "lock=>" + b);try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}synchronized (b) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "lock=>" + b + "lock=>" + a);}}}
}解决问题
1、使用 jps -l 定位 进程
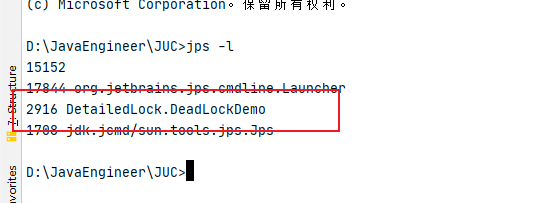
2、 使用jstack+进程号 2916
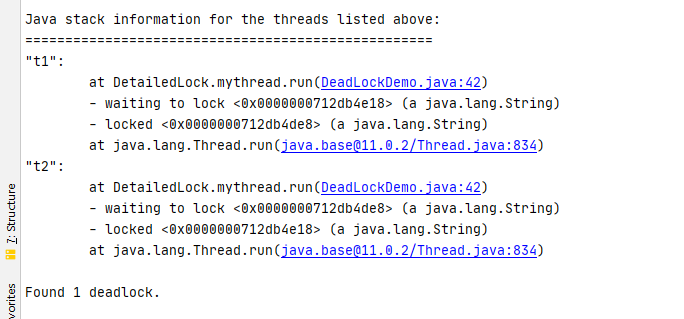
面试或者工作中,排查锁的问题:
- 日志 百分之九十
- 堆栈 百分之十